Page Navigation
Long Lasting, High Precision, Low Maintenance
Download the Roller Screw Brochure
Choosing to work with Tolomatic for high force linear actuators means understanding the application specifics and choosing the right technology for the job. Tolomatic does not take a “one technology” approach to solving customer needs and can provide industry best sizing & selection, application advice, quality, pricing, delivery (15 days) and after market service (free, quick evaluation) on both roller screw and ball screw linear actuators for high force applications.
Start learning now with our guide to actuator screw technology, Selecting the Optimal Screw Technology. Or, download our e-Book on A Resource on Electric Linear Actuators: What a machine builder needs to know. For intelligent, helpful advice on linear actuator selection, contact us or your local Tolomatic distributor.
Tolomatic offers a range of high-force electric linear actuators, all with long-lasting standard planetary roller screws

Roller Screws
Verified and tested extensively
Proven long, reliable life
Configurable stroke lengths

RSX Extreme Force Electric Rod Actuators
Roller screw driven
Forces up to 40,000 lbf (178 kN)
Flexible motor mounts

RSA-HT Heavy Duty Electric Rod Actuators
Add any servo motor
Forces up to 13,039 lbf (58 kN)
Economical ball screw options
ServoWeld® Resistance Spot Welding Actuators
Multiple designs for various weld guns
20+ million welds
Superior welds & force repeatability

IMA Integrated Servo Motor Actuators
Integrated servo motor design
Forces up to 6,875 (30.6 kN)
Compatible with many servo drives
IMA Food Grade Linear Actuators
Food Grade white epoxy coating
Forces up to 6,875 lbs (30.6 kN)
IP67 rating

RSH Hygienic Electric Rod Style Actuators
316 Stainless Steel Construction
Forces up to 7,943 lbf (35.3 kN)
IP69k, clean-in-place
Planetary (standard) roller screw linear actuators
Roller screws (also called planetary roller screws) have precision-ground threads that match multiple precision-ground rollers in the nut. These rolling elements transmit force very efficiently. Roller screw components provide more points of contact allowing for higher force capability and longer life.
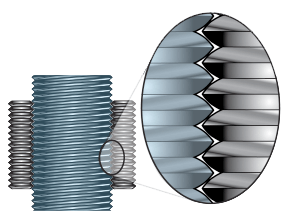
The use of planetary roller screws is allowing engineers to specify electric actuators in applications that were previously dominated by hydraulic cylinders.
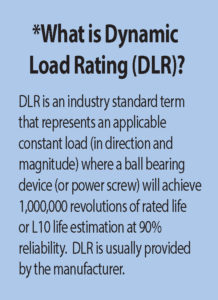
Tolomatic manufacturers standard roller screws for its actuators. These screws are case (surface) hardened before precision grinding, resulting in very deep case hardness and high Dynamic Load Rating (DLR*.)
How to select the correct screw choice for high force linear actuators: Standard Planetary Roller Screws, Inverted Roller Screws, or Ball Screws
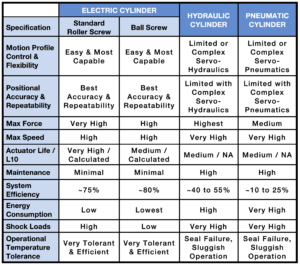
There are several screw technology options to consider when specifying high force electric linear actuators – standard planetary roller screws, inverted roller screws and ball screws. Each technology has its advantages and disadvantages when compared to one another.

To select the best option, it is critical to let the application specifications be the guide. Some companies only sell ball screw linear actuators and some companies only sell roller screw linear actuators. Take caution when evaluating “there is only one technology” type vendors. Every application is different and both technologies (roller screw and ball screws) have their place. By evaluating the application details and both technologies, it will ensure you optimize performance and cost.
Tolomatic manufacturers both roller screw and ball screw high force electric linear actuators. Tolomatic’s online electric actuator sizing software guides engineers through the application specifications including force, speed, dwells, life estimates and other factors in order to make the correct choice.
Standard Planetary roller screws offer the highest dynamic load rating for the longest life of the three technologies. Both roller screw technologies are good choices for repeated stress applications in same area of actuator stroke. Applications such as pressing, inserting, riveting are applications with repeated stress. Roller screws have significant increase in contact area which allows for longer life and exerts higher forces in the same package size versus ball screws. However, this increased contact area also creates more heat with the same amount of work. Ball screws, because they have less contact points, are a little more efficient in heat management than roller screws which allows them to operate cooler in high duty cycle and high speed applications. Heat management is a major factor in how well lubricants hold up over time and whether the actuator/screw choice can last as long as expected. There are other factors in each screw technology deployed in an actuator that determines their advantages and disadvantages. See the comparison table below.
Inverted roller screw linear actuators
An inverted roller screw operates much the same as a standard roller screw except the functions of the nut and screw are reversed. The rollers move inside the nut.
Most inverted roller screws used in linear actuators are produced using a process other than grinding to inexpensively create threads inside the nut. The hardening process is performed after the nut is machined and results in a much shallower case hardness depth and softer threads than those of standard roller screws. This leads to a significantly lower DLR* (lower life) and more challenges with maintaining lubrication.
Standard Planetary Roller Screw vs. Inverted Roller Screw
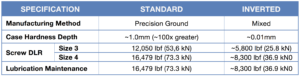
The chart above reflects integrated servo actuators with standard and inverted screw designs. The DLRs listed here are selected from like-sized product.
By utilizing the inverted design in an actuator, the actuator may be a little more compact than an actuator with a standard roller screw, but this comes at a sacrifice of lower DLR (lower life). Because of this, Tolomatic only supplies actuators with standard planetary roller screws to maximize service life.
Ball screw linear actuators
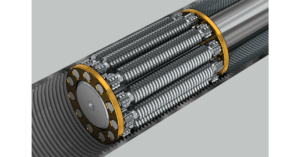
Ball screws get their name from the re-circulating ball bearings that fit between arch-shaped screw threads and corresponding threads in the nut. The ball bearings transmit force and relative motion efficiently as they roll through one or more circuits in the nut.

Ball screw actuators have higher thrust capabilities, longer service lives and higher efficiency than those with acme screw systems, but they can’t match the performance of roller screw actuators. Ball screw actuators can be back-driven and can be noisy. They’re ideal for applications that require high duty cycles, moderately high thrust and moderate speeds. They tend to be reasonably priced, making them popular in many applications. When it comes to comparing roller screw vs ball screw of similar size and lead, a ball screw’s ball bearings have fewer points of contact than roller screws as shown in the diagram below…

This, plus a design that allows the bearings to contact each other, limits the ball screw’s DLR*, leading to lower forces and shorter life.
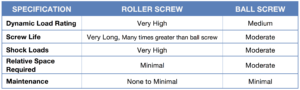
For most applications that require high force, repetitive cycles and long expected life, Tolomatic will recommend a roller screw linear actuator. However, if the force is lower and high continuous speeds are present in the application, Tolomatic may recommend a ball screw actuator.

 Ask an Engineer
Ask an Engineer
